An overview of analog and digital synth design, its components and how they work.
This article list the essentials in subtractive synthesis design and programming.
Synthesizer programming and Sound design and how to program
Programming synthesizers require basic knowledge of the different modules used to build it.
This article explains the most important modules with programming tips.
What is Subtractive Synthesis?
Subtractive synthesis is a synthesis method where oscillators generates waveforms and then filter out frequencies over time to make the sound interesting and evolving.
oscillators
An oscillator is the waveform generator in almost all analog keyboard designs. It has a limited number of waveforms and on some synths like the famous Prophet 5 they can be combined.
The simple waveforms:
- Sine
- Triangle
- Saw
- Square
- Noise
A synthesizer can have 1 to many oscillators per voice but 2 or 3 is typical on an analog synth.
In synths the oscillator abbreviation is:
- VCO for Voltage Controlled Oscillator. In software VCO is actually a DCO since no voltage is involved but virtually we can still see it as VCO.
- DCO for Digitally Controlled Oscillator. DCO is the digital version of VCO.
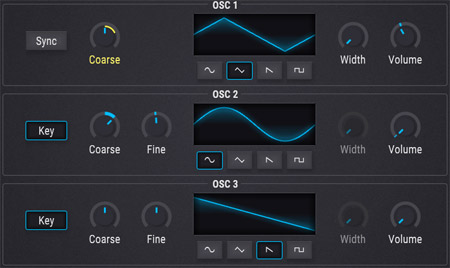
Arturia Pigments analog oscillators
 Minimoog oscillators. 3 VCOs. In software VCO is actually DCO.
Minimoog oscillators. 3 VCOs. In software VCO is actually DCO.
 The VCO 1 and VCO 2section on a Roland Jupiter 8 Synth
The VCO 1 and VCO 2section on a Roland Jupiter 8 Synth
Cross modulation
Cross modulation is a design where one oscillator can modulate another one. This is effective for generating overtones and sounds outside the fundamental frequency.
 Cross Modulation on VCO 1 on a Jupiter 8
Cross Modulation on VCO 1 on a Jupiter 8
Roland Jupiter 8 has Cross Modulation where VCO 1 can be modulated by VCO 2 for interesting sounds.
Envelope
An envelope is a time-based controller used a lot in synthesizers.
ADSR is a typical envelope containing 4 points. Attack, Decay, Sustain and Release. Some synthesizers has a Hold stage too.
Envelopes are typically used in the filter and amplifier to modify sound over time based on keyboard events (Note on)
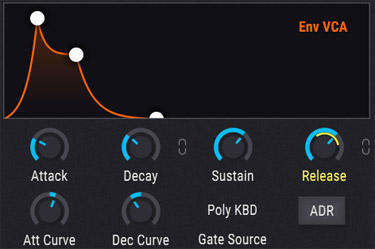
A modern Pigments Envelope
Modern software synthesizers has more control over the envelops than older analog units had. Arturia Pigments has curves on attack an decay for non linear control.
Filter
The filter is an important part of any Subtractive Synthesis.
The filter is typically controlled by an ADSR envelope with an amount that contols its impact on the sound.
In synth the abbreviation is:
- VCF for Voltage Controlled Filter
- DCF for Digitally Controlled Filter
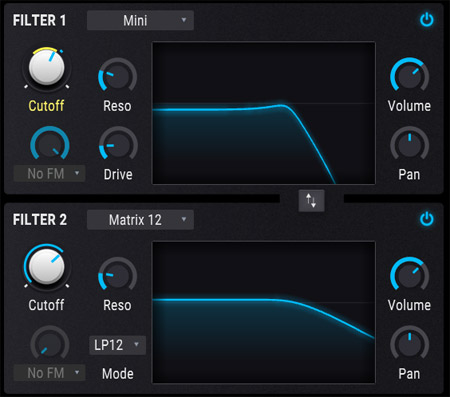
Arturia Pigments Filters VCF
Filter modulation
The filter can be controlled and modulated by an envelope amount for time based changes.
Amplifier
Amplifier or in short amp is the gain stage used in a lot of electrical instruments. Amp controlls the volume and amp velocity. VCA stands for Voltage Controlled Amplifier.
LFO
Low-Frequency Oscillator or LFO is essentially the same as the sound generating oscillator but it has a much lower frequency.
It is typically used as a controller for modulating parameters to make a sound change over time.
Arturia Pigments LFOs for modulation
LFO is often used to pitch- or filter modulate the sound. Tremolo, Vibrato, and Auto pan is essentially done with an LFO.
Wavetable
A Wavetable is like a digital oscillator that generates complex waveforms instead of the simple waveform Oscillators.
It is actually a list of samples (called a table) that can be morphed over time.
Some wavetable based synthesizers:
- Access Virus TI
- Waldorf Quantum
- Waldorf Blofeld
- Steinberg Halion
- Arturia Pigments
- NI Massive/Massive X
- Xfer Serum
Modulation
Modulation is a way to make the sound interesting over time.
Modulation uses a source to modulate a parameter.
Some modulation sources:
- Velocity
- Aftertouch
- LFO
- Envelope
- Mod Wheel
- Modulation Macros
- Functions
- MIDI continuous controls (CC)
A modulation source can modulate another source for complex modulation.
For example 2 LFOs modulate each other.
Arpeggiator
Arpeggiator is a sequencer like a feature that triggers held notes one at a time in time with the tempo. It is a way to play chords on monophonic synthesizers and can create interesting patterns. Combined with modulation one can create interesting musical patterns.
How to program synthesizers
Programming synthesizers is a lot easier when you know the basic modules of a generic synth. The term programming refers to setting parameters and no code actual language is needed.
There might be differences in your synths but still they have the same overall components.
It is usually not that hard to learn but easier to program a new synth if you already know and program your own presets on a few synths.
Where to start?
basic preset steps in how to program:
- Set the Oscillators
- Set the Envelopes
- Set the Filters
- Set the LFOs
- Modulate Oscillators and Filters with the Envelopes and/or LFOs
It takes a lot of practice to program a specific sound from the top of your head or from listening to other artists music. A good understanding of the audio signal path and the components in runs through is always a help.
Drum programming
Drum programming is related to synth programming and related to sound design. It can be done on a synthesizer or sampler.